Co2 Laser Beam Width

Insert the mahoney beam visualization tool into the first beam bender.
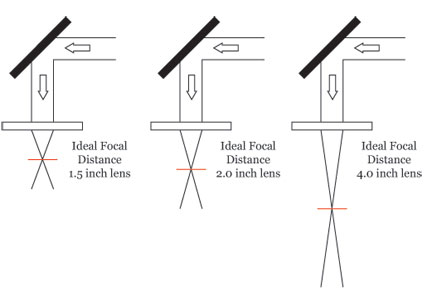
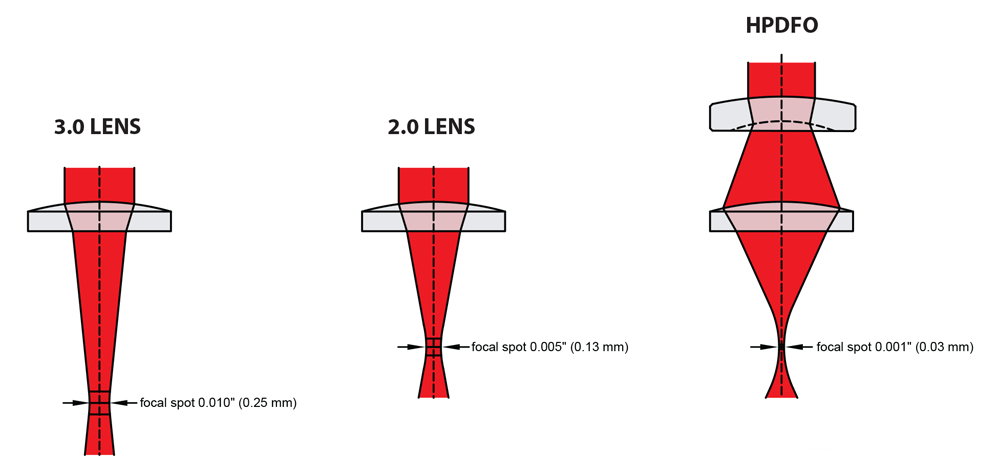
Co2 laser beam width. Therefore if our laser beam is 6 mm wide and we use a 6 mm diameter 6 mm focal length zese meniscus lens not very common the beam could measure 0 1 mm 100 micron in diameter. The divergence of a laser beam can be calculated if the beam diameter d 1 and d 2 at two separate distances are known. Things have changed however with the introduction of spiricon s new beamwatch which measures laser beam width and focal length of any laser beam without attenuation. If you have the camera option then look at the target on your computer.
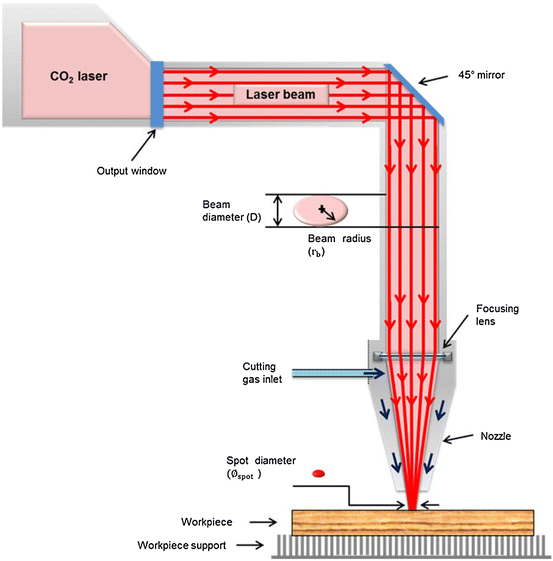
Turn on the co2 laser and adjust the laser power so that the laser beam is visible and not too bright on the side viewport. The wavelength for a co2 laser beam is roughly 10 microns or 01mm. It was invented by kumar patel of bell labs in 1964 and is still one of the most useful. Examine the location of the raw co2 laser beam in relation to the cross hairs.
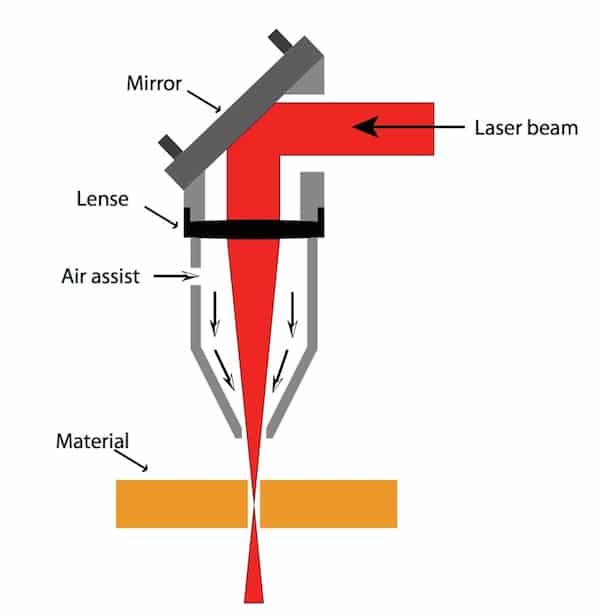
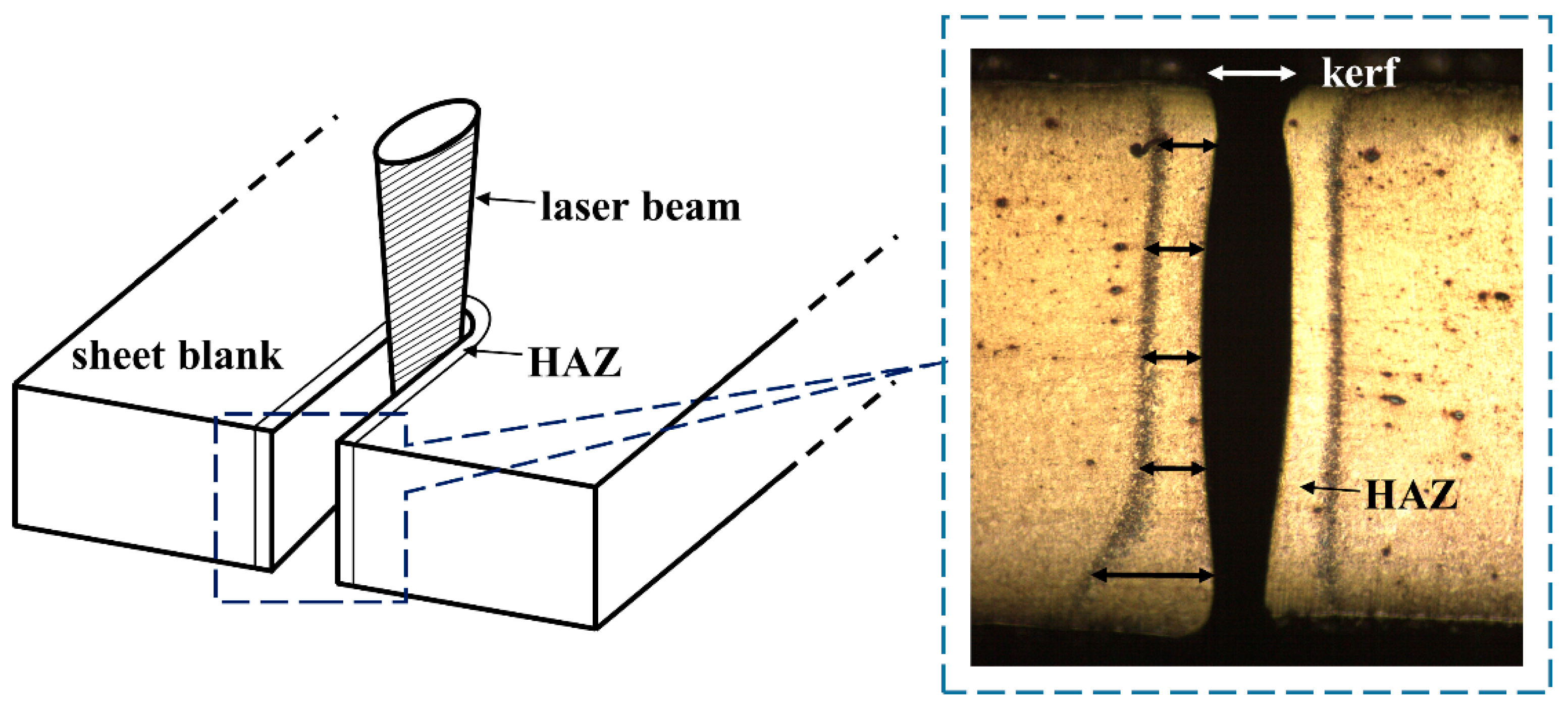
Carbon dioxide lasers are the highest power continuous wave lasers that are currently available. How to make laser beam alignment. The power density of a tightly focused industrial laser can be quite high. Laser tubes producing an out of round or oval shaped beam will degrade the cutting and engraving quality substantially.
These lasers can maintain continuous and very high levels of power and are typically used in cutting welding etching and marking applications. The co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering on 9 6 and 10 6 micrometers. Usually divergence angle is taken as the full angle of opening of the beam. When you change mirrors len laser tube laser beam path route may go in misalignment and not straight.
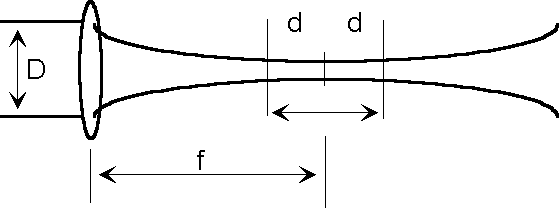
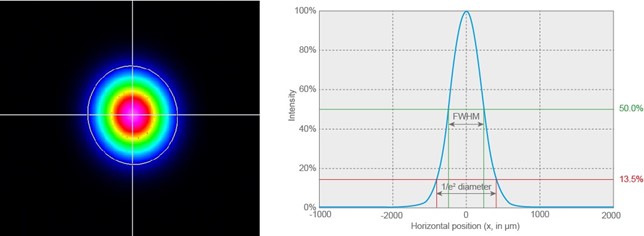
Where w 0 is the beam waist the smallest radius of the gaussian beam and z r is the rayleigh length. This video teaches you how to adjust the laser beam. If we consider the ideal case of a gaussian beam the beam width or radius w along the propagation axis z is defined by the following equation. Note that in the example we chose znse as our lens material and meniscus as its shape good for co 2.
This probably seems too good to be true. But to maximize the power and clarity of your laser cutting and engraving the laser beam spot size has to be clean small and as round as the laws of physics will allow. Let z 1 and z 2 are the distances along the laser axis from the end of the laser to points 1 and 2. The carbon dioxide laser was one of the earliest gas lasers to be developed.
When a laser beam propagates along its optical path its diameter is continually changing.